SASS precompilation
Table of contents
- Add SASS precompilation to your web app
- Customize settings
- Activate the same workflow for mobile apps
Add SASS precompilation to your web app
We will see how to add SASS files precompilation to the build process. You should read the Build process introduction first.
First we need to add to our package.json the following dependency:
{
"devDependencies": {
"gulp-sass": "*"
}
}
Then add the source and the destination folders to the paths variable defined in the gulpfile.js, as it follows:
var paths = {
// ... html, js and css folders
sass: {
src: [baseFolder + 'scss/**/*.scss'],
dest: baseFolder + 'styles'
}
};
Now import the gulp-sass dependency and create a Gulp task named sass with the following code:
var sass = require('gulp-sass');
gulp.task('sass', function(done) {
gulp.src(paths.sass.src) // define sources location
.pipe(sass()) // start sass process
.on('error', sass.logError) // halt on errors
.pipe(gulp.dest(paths.sass.dest)) // copy css into destination
.on('end', done); // quit
});
Finally, enable the watch task to look for any file change under the app/scss folder with sass and reload tasks as second parameter:
gulp.task('watch', function() {
gulp.watch(paths.sass.src, ['sass', 'reload']);
gulp.watch([
// ... html, js and css folders
], ['reload']);
});
This way the Gulp watch task will now also trigger the sass sources precompilation and the live-reload event.
Note: If a Gulp process was already running you must close and re-open your solution to reload the configuration.
Customize settings
A working sass task is now part of the build. We can improve it with additional functionalities:
SASS options
SASS options can be set passing a parameter object to the sass() function:
gulp.task('sass', function(done) {
gulp.src(paths.sass.src)
.pipe(sass({
outputStyle: 'compressed' // produce compressed output
}))
.on('error', sass.logError)
.pipe(gulp.dest(paths.sass.dest))
.on('end', done);
});
SASS compressed output helps to reduce the filesize.
Minify and rename files
A complete minification can reduce the filesize even further:
var minifyCss = require('gulp-minify-css'),
rename = require('gulp-rename');
gulp.task('sass', function(done) {
gulp.src(paths.sass.src)
.pipe(sass())
.on('error', sass.logError)
.pipe(minifyCss()) // clean and minify *.css files
.pipe(rename({ extname: '.min.css' })) // rename *.css to *.min.css
.pipe(gulp.dest(paths.sass.dest))
.on('end', done);
});
Note: this functionality requires the following dependencies to be defined in the package.json file:
{
"devDependencies": {
"gulp-minify-css": "*",
"gulp-rename": "*"
}
}
Both compiled and minified versions
In order to produce both a compiled and a minified version at the same time edit your sass task as follows:
var minifyCss = require('gulp-minify-css'),
rename = require('gulp-rename');
gulp.task('sass', function(done) {
gulp.src(paths.sass.src)
.pipe(sass())
.on('error', sass.logError)
.pipe(gulp.dest(paths.sass.dest)) // copy *.css to destination
.pipe(minifyCss())
.pipe(rename({ extname: '.min.css' }))
.pipe(gulp.dest(paths.sass.dest)) // copy *.min.css to destination
.on('end', done);
});
Note: this functionality requires the following dependencies to be defined in the package.json file:
{
"devDependencies": {
"gulp-minify-css": "*",
"gulp-rename": "*"
}
}
Sourcemaps
In order to add sourcemaps edit your sass task as follows:
var sourcemaps = require('gulp-sourcemaps');
gulp.task('sass', function(done) {
gulp.src(paths.sass.src)
.pipe(sourcemaps.init()) // generate sourcemaps
.pipe(sass())
.on('error', sass.logError)
.pipe(sourcemaps.write()) // write sourcemaps into *.css
.pipe(gulp.dest(paths.sass.dest))
.on('end', done);
});
Note: this functionality requires the following dependencies to be defined in the package.json file:
{
"devDependencies": {
"gulp-sourcemaps": "*"
}
}
You can now found your sourcemaps inside the output file as a comment:
/*# sourceMappingURL=data:application/json;base64,eyJ2ZXJzaW9uIjo...
Minify and rename, original and source maps
The combination of all:
var sourcemaps = require('gulp-sourcemaps'),
minifyCss = require('gulp-minify-css'),
rename = require('gulp-rename');
gulp.task('sass', function(done) {
gulp.src(paths.sass.src) // define sources location
.pipe(sourcemaps.init()) // generate sourcemaps
.pipe(sass()) // start sass process
.on('error', sass.logError) // halt on errors
.pipe(sourcemaps.write()) // write sourcemaps into *.css
.pipe(gulp.dest(paths.sass.dest)) // copy *.css into destination
.pipe(minifyCss()) // clean and minify *.css
.pipe(rename({ extname: '.min.css' })) // rename *.css to *.min.css
.pipe(sourcemaps.write()) // re-write sourcemaps into *.min.css
.pipe(gulp.dest(paths.sass.dest)) // copy *.min.css to destination
.on('end', done); // quit
});
Note: this functionality requires the following dependencies to be defined in the package.json file:
{
"devDependencies": {
"gulp-minify-css": "*",
"gulp-rename": "*",
"gulp-sourcemaps": "*"
}
}
Activate the same workflow for mobile apps
We will now evaluate how to integrate the same workflow in our Wakanda Ionic-based mobile application. Inside the mobile folder you can find a gulpfile.js file. However this build process is slightly different:
- Ionic includes a live-reload mechanism for
wwwfolder. Thus a Gulp live-reload implementation is not necessary. - Ionic already includes a snippet of code to support SASS precompilation.
- Ionic takes into consideration only the Gulp tasks defined in the
ionic.projectfile. - Node.js modules are not installed by default in the
mobilefolder.
In order:
1 - Add to the package.json inside your mobile folder any Gulp dependency you may need. Following the example above we will need to add only gulp-sourcemaps to the dependencies already provided:
<img src="img/mobile-scss-json-sourcemaps.png" />
2 - Run in the terminal npm install while inside your mobile folder to install all the Gulp and SASS dependencies defined in the package.json file.
3 - Create a scss folder inside the mobile folder and put our sass sources inside:
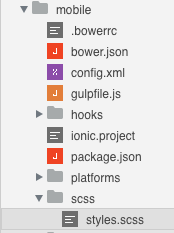
Being outside of the www folder, SASS sources won’t included in the final application package.
4 - Customize the sass task inside the gulpfile.js to be coherent with your project scaffolding:
// 1 - change sass paths like this
var paths = {
sass: {
src: ['./scss/**/*.scss'],
dest: './www/css/'
}
};
// 2 - add missing require
var sourcemaps = require('gulp-sourcemaps');
// 3 - add missing tasks
gulp.task('sass', function(done) {
gulp.src(paths.sass.src)
.pipe(sourcemaps.init())
.pipe(sass())
.on('error', sass.logError)
.pipe(sourcemaps.write())
.pipe(minifyCss())
.pipe(rename({ extname: '.min.css' }))
.pipe(gulp.dest(paths.sass.dest))
.on('end', done);
});
gulp.task('watch', function() {
gulp.watch(paths.sass.src, ['sass']); // 'reload' task is not necessary
});
5 - Finally, tell Ionic which Gulp tasks you want to run. Add this line inside the ionic.project file:
"gulpStartupTasks": ["sass", "watch"],
6 - Now click on any mobile action button (for instance Preview). If the configuration is correct you should see the following output in the console:
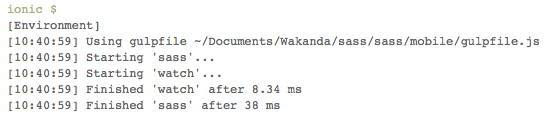
and when saving your sass sources:

Note: If a Ionic process was already running you must close and re-open your solution to reload the configuration.